
Each of us has probably heard about what is a trader, but let's make sure we use these words correctly. Traders carry out transactions on various financial markets, aiming to make profits.
There are many varieties of trading and trading strategies that can be applied to speculation. However, to use them successfully, anyone should take a series of actions or steps that will help to become a trader.
In this article, we will delve into the definition of a trader, what their activities include, how much they can earn, and many other questions.
What is a trader in essence
So, what is a trader and what do they do? Let's try to understand what exactly the profession of a trader means and what its key features are.
We have already mentioned that a trader is a market participant who conducts transactions in financial markets. Moreover, they can do this on their own or on behalf of another person or organization. Traders who manage trades on behalf of other individuals or entities are referred to as institutional traders.
Every trader can buy or sell various financial assets, known as trading instruments. These include stock indices, currency pairs, company shares, bonds, metals, energy commodities, and others.
The main goal of a market participant is to make a profit from the difference in the asset’s price at the time of buying and the time of selling. Depending on whether a trader intends to buy or sell an asset, there are different types of trading:

- Bulls, or buyers, are market participants who buy assets, betting on an increase in their market quotes after a while. It is the buyers who drive the price of the asset up, intending to sell it at a higher price later.
- Bears, or sellers, are traders who anticipate a decrease in the asset's value. They push the price of the asset down, with the intention of buying it back at the lowest possible price later.
Typically, bulls engage in long trades, which are transactions buying a particular asset. On the other hand, bears enter into short trades, which means selling.
Importantly, the duration for which positions are opened has no relation to their names. Positions can be opened for periods ranging from a few seconds to several months. We will discuss various options and timeframes for opening positions in the next section.
Types of trading
Each market participant sticks to a certain trading algorithm which corresponds most to their personal preferences. There are several popular trading strategies.
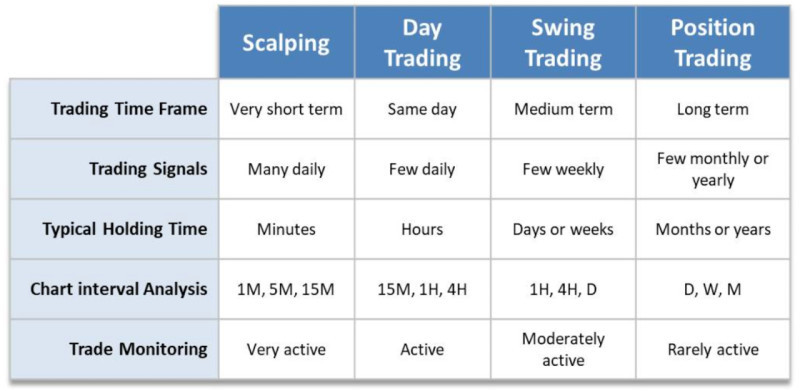
Наиболее общее деление включает в себя три основных вида трейдинга:
1.The most common division includes three main types of trading:
- Short-term trading involves executing trades within a single trading day. The number of trades and their duration can vary depending on the sub-type within this category.
- High-frequency trading. Trades are executed in fractions of a second. This type of trading is not accessible to humans and is performed exclusively by specialized automated programs.
- Scalping. Trades are opened for a period ranging from a few seconds to a few minutes. Scalpers aim to make a small profit on each trade but execute a large number of trades, sometimes reaching several hundred in a single day.
- Intraday trading. Positions are opened and closed within one trading day, with no overnight positions. On average, traders make from 4 to 8 trades per day.
- 2. Medium-term trading involves trades with a duration ranging from several days to several weeks. This type is also known as swing trading because it relies on fluctuations in market quotes. The number of trades could be from 2-3 trades per week to 3-4 trades per month, each potentially yielding a profit of 30-50 pips.
- 3. Long-term trading implies holding positions for several months to several years. This type of trading is also known as investing as funds are "frozen" for a relatively long period. The primary goal of long-term traders is to profit from the increase in the asset's value over time.
Trader versus investor: how they differ
Traders and investors have a lot in common, but they also have a number of quite significant differences. What both have in common is that they are trying to profit from changes in the price of an asset.
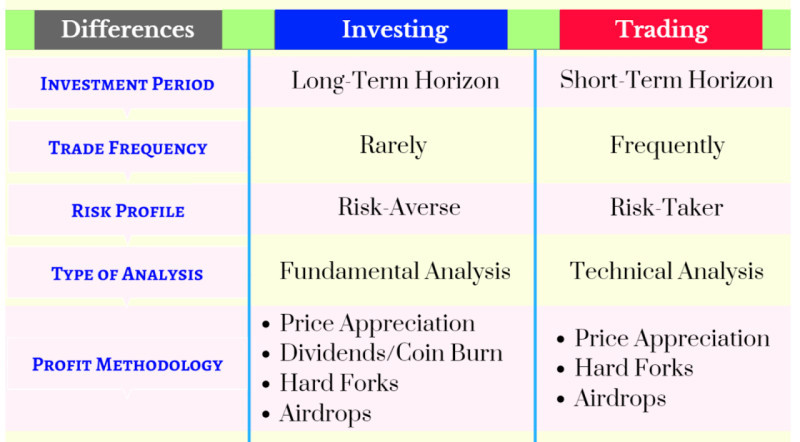
1. The first and one of the most significant differences is the planning horizon. Traders are primarily concerned with what will happen to an asset in the near future, whereas investors try to puzzle out what changes will happen in the asset’s value in the long term.
2. Market analysis. Traders mainly use technical analysis, where the key element is price and its fluctuations. Investors give priority to fundamental analysis, examining all factors that may influence an asset in the future.
3. Asset selection. Traders focus on choosing highly volatile assets, whose prices display constant fluctuations, for instance, currency pairs. Investors seek undervalued instruments that will appreciate in value over time, such as stocks of mining companies.
4. Risk and reward ratio. It is believed that traders are exposed to higher risks than investors. At the same time, they can achieve more significant profits and continue trading, effectively multiplying their capital. Investors commit funds for the long term and "freeze" them without the option of immediate withdrawal.
5. Initial investments. To start trading and generate profits, traders do not need substantial initial investments. Modern trading platforms allow traders to get started with as little as $1. Investors, on the other hand, require a relatively large initial capital, typically starting from $1,000 and above.
6. Time commitment. Oftentimes, traders, especially those who prefer short-term trading, need to spend a significant amount of time monitoring constant price fluctuations. Investors invest their money at once, and they do not need to monitor the market nonstop.
How to become what is a trader
Becoming a trader is something that anyone can do, but it requires taking several steps, including finding a broker. A trader vs broker are an inseparable combination without which engaging in trading is impossible.
Let's go through the steps that a person needs to take before getting into trading:
- Determine your trading profile. This includes goals in trading, age, the amount of free time, initial investment size, risk tolerance, and some other parameters.
- Get trained. Currently, there are many opportunities for training. You can study materials from the internet on your own, take online or offline courses, attend lectures, webinars, and more.
- Define a trading strategy. A trader needs to have a trading algorithm that incorporates all the essential trading rules. However, developing your own system can be challenging in the beginning, so you can resort to available strategies.
- Choose a broker. This is an intermediary that grants retail traders access to financial markets. Brokerage companies differ in the conditions they offer to clients: the number of trading instruments, funding and withdrawal options, commission rates, and more.
- Download a trading platform. Choosing a trading platform is an important step in trading. There are platforms developed specifically for certain brokers, available only to their clients, as well as universal trading platforms developed by third-party companies.
- Practice on a demo account. Before starting real-money trading, it's better to test your skills on a demo account. It looks just like a live account but allows trading with virtual funds.
- Begin trading on a live account. After profitable trading on a demo account and gaining an understanding of how it all works, you can start trading on a live account.
Where and how to learn
As mentioned earlier, to succeed in such a serious endeavor as trading, education is an important stage that cannot be skipped. There are numerous options for training, and let's consider the main ones.
- Self-education: This is a budget-friendly option but not a fast one, as you have to find all the information yourself. However, there is no problem with this because there is a vast amount of information available online. Self-education includes:
- - Studying articles on the Internet, but it's important to pay close attention to their authors and content. It's crucial to understand that there is a lot of unreliable information online that can mislead novice traders.

- Reading specialized books: Traders with many years of experience and significant capital gained from trading in financial markets are often willing to share their trading strategies and methods. Many of these books can be found and downloaded for free on the Internet.
• Broker-provided education. Almost every brokerage company offers some form of learning course before their clients make a debut in trading. Oftentimes, these courses are provided for free when opening an account with the broker.
• Courses, lectures, webinars by renowned traders. Access to these resources is typically offered on a paid basis, with some cases providing a free trial lesson. These can be used as options for additional education after self-study of the subject or gaining more in-depth knowledge about a specific strategy, asset, and so on.
• Personal education/advice. You can seek advice from experts and receive personalized recommendations regarding which types of trading are most suitable for a specific user, taking into account their individual features and abilities.
Trading strategy
Let's take a closer look at another important aspect, i.e. the choice or development of a trading strategy. The world's best traders wouldn't have become successful without having a personal trading algorithm.
As mentioned earlier, it can be quite challenging for novice traders to develop their own strategy initially, so they can try using ready-made algorithms.
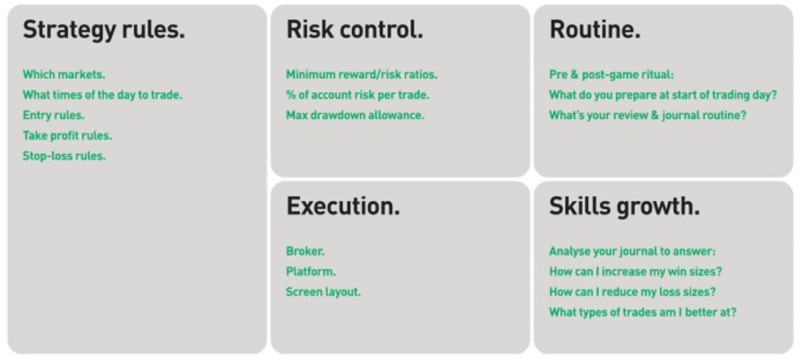
A trading system includes a set of crucial rules:
- For market analysis
- For entering a trade
- For holding positions
- For exiting a trade
- Loss limitations
- For risk and money management
A trader needs to determine the most suitable methods for market analysis. Some users rely solely on the chart itself and its patterns, finding graphical and candlestick patterns on it. Others use additional tools, such as technical indicators, to generate signals.
By rules for entering the market, we mean the conditions for opening positions. Previously, a trader has to recognize a signal from the analytical tools in use. Speculators frequently combine several tools to confirm the accuracy of the signal.
There are two options for exiting trades: manually or automatically. Often, positions are closed by means of pending orders, which simultaneously act as stop-losses or profit targets.
Rules for risk and money management make traders determine what portion of the total deposit volume should be used for each trade. As a general rule, it is recommended not to risk more than 3-5% of the deposit per one trade. However, variations are possible.
A very important element of any trading strategy is its adjustment to the trader's character traits, personality, and other individual features. We will discuss this a bit later.
Following clearly defined the above-mentioned rules greatly facilitates the trader's work. However, for successful trading, it is not enough to just develop these rules. It is also essential to strictly adhere to them in any situation.
Sticking to the rules of an individual trading algorithm allows the trader to experience less stress and make fewer impulsive emotional trades. As a result, this positively affects the balance of the trading account as more profitable trades are executed than losing ones.
Types of trading strategies
There are three main types of trading strategies:
- Trend-following strategies;
- Counter-trend strategies;
- Range-bound strategies.
Trend-following strategies are used when the asset's price follows a clear-cut direction in the market. The key idea of such algorithms is that price is more likely to continue in the same direction than to reverse it. During an uptrend, long positions are opened. Alternatively, during a downtrend, short positions are taken. A further uptrend is confirmed when the price prints higher lows and higher highs on the chart, whereas a downtrend is distinguished by lower lows and lower highs.
Counter-trend algorithms are also used during directional price movements. However, positions are opened in the opposite direction during periods of corrective price movement, which means a small retracement in the opposite direction. Even during the most powerful trend movements, there are sometimes "breathers" when the price retraces slightly. It is during these corrections that positions can be opened against the current trend: selling during an uptrend and buying during a downtrend.
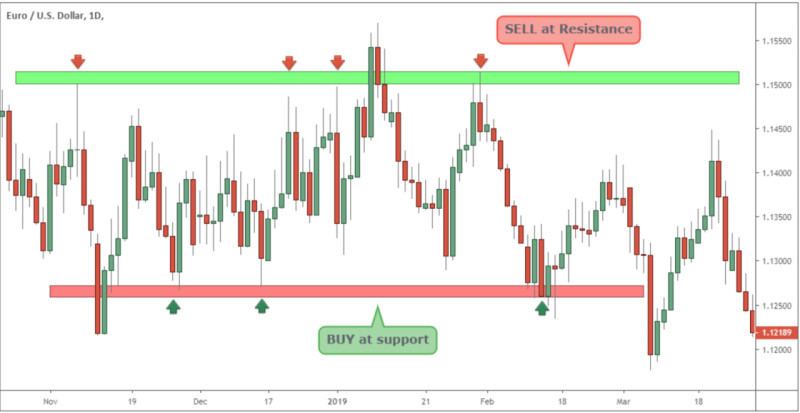
Range-bound strategies are used when the asset’s price moves within a range bounded by support and resistance levels. With such a movement, the price can repeatedly oscillate between the upper and lower borders, kick out of them, and again continue to move within the range.
There are two main trading methods applied here: a bounce/dip and breakout. In the first case, positions are opened when the price touches one of the borders: when the lower border is touched, a trader goes long and when the upper one is touched, a trader goes short. Breakout strategies involve opening positions during a breakout through one of the borders.
Types of traders’ temperament
The psychological component is an important element of trading which should not be neglected. After all, how much a trader earns is inextricably linked to whether the strategy is correctly selected for their type of temperament.
Temperament is a set of certain innate human properties which does not change throughout their life. There are four main types of temperament:
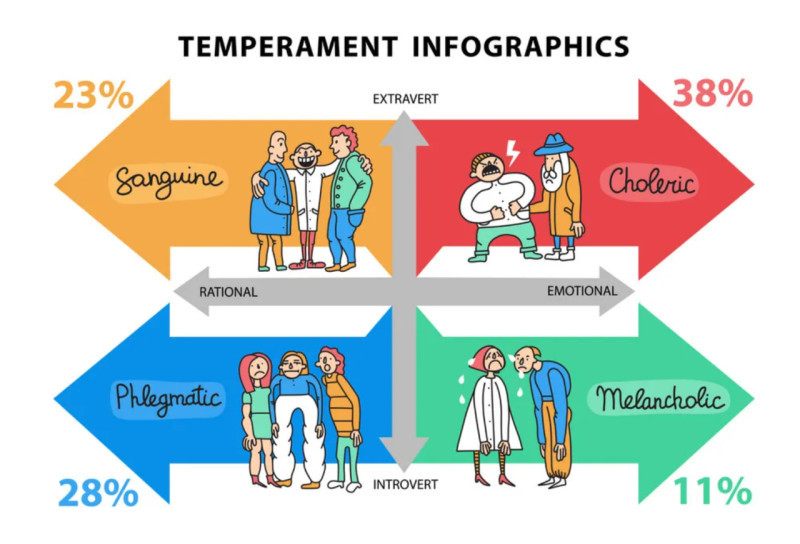
- Sanguine is optimistic, cheerful, energetic, and stress-resistant.
- Melancholic is pessimistic, sensitive, cautious, uncertain, struggles with stress.
- Phlegmatic is slow-paced, focused, stress-resistant, and patient.
- Choleric is impulsive, active, energetic, emotional, and adventurous.
Interestingly, choleric and sanguine individuals are considered extroverted types, while melancholic and phlegmatic individuals are assigned to introverted ones. In terms of emotional stability, sanguine and phlegmatic individuals are more stable, while melancholic and choleric individuals are less stable.
Certainly, "pure" temperaments are quite rare, and most individuals have a mixture of several temperaments. However, one of them typically prevails and has a stronger influence on a person's behavior.
When it comes to trading, different temperament types are more suited to certain strategies due to their key features. Let's take a closer look at which strategies are suitable for each type.
So, sanguine individuals are best suited for day trading and medium-term trading. They cannot wait for results for too long, so long-term trading is not suitable for them. However, they need to control their optimism and overconfidence in order to objectively assess the situation and all the risks.
Melancholic individuals may find it challenging to engage in trading due to their pessimism and lack of stress tolerance. However, thanks to their analytical abilities and a willingness to work on their mistakes, they can become good strategy developers.
Phlegmatic individuals are more inclined toward long-term trading, as they make decisions very thoughtfully and slowly. In addition, they lack the thrill-seeking behavior needed for quick trades. However, they possess excellent stress tolerance.
Choleric individuals are well-suited for short-term trading, often opting for scalping. They can make quick decisions and are adventurous, but they tend to act impulsively, which can hinder their trading.
How to choose broker
To access financial markets, traders need an intermediary, and this intermediary is a brokerage company. To avoid future problems, it's essential to take the broker selection seriously. When choosing a broker, pay attention to several important factors:
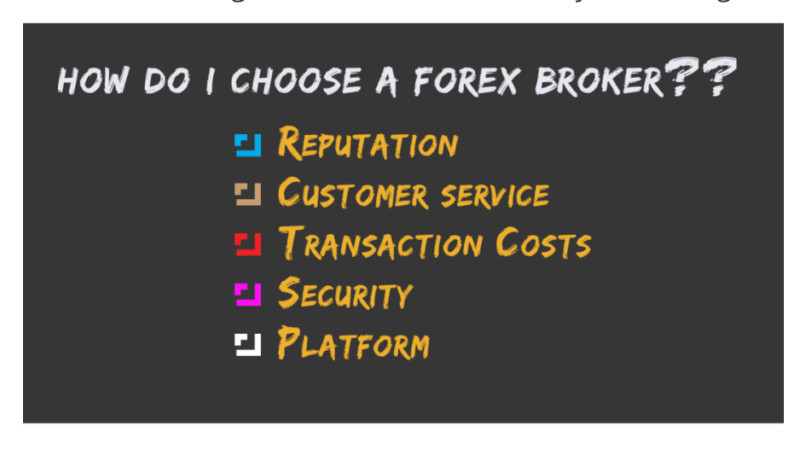
- Reliability. The brokerage company should have a license and comply with the regulations of the country in which it is registered. Besides, find out about the company's experience and the number of clients it has.
- Reputation. Research reviews from other users about the company on various websites. Be cautious if you only find positive comments, as they may be fake or paid for. An honest broker is transparent about both their strengths and weaknesses.
- Trading instruments. Find out which financial markets the broker operates on as this will allow you to trade on multiple markets simultaneously. If you already know which asset you want to trade, look for a leader in that area.
- Types of trading accounts. Find out whether the broker offers the option to open a demo or cent account to practice trading without risking real funds. Additionally, the company may provide various account types suitable for different trading strategies.
- Commission rates. Commissions charged by brokers for executing trading operations are referred to as spreads. Some companies offer fixed spreads, while others offer variable spreads that can change based on trading volumes.
- Leverage. Traders, especially in the Forex market, often use leverage, i.e. borrowed funds from the broker. The size of the leverage varies between companies and account types.
- Customer support and service. Find out how quickly and efficiently orders are executed, how deposits and withdrawals are processed, and how responsive customer support is in resolving any issues. A broker's ability to handle these aspects smoothly is crucial.
- Training. Major brokerage firms often offer learning resources in the form of online training and courses. Access to these courses is often provided for free upon opening an account. Additionally, brokers regularly publish analytical reviews and fresh news on their websites.
How to choose trading platform
Regardless of the type of trading a trader prefers, whether it's short-term or long-term, swing trading, or scalping, they will need a trading platform to execute all trading operations.
So, a trading platform is software that allows traders to access financial markets and execute trading operations. To trade directly, as mentioned earlier, a trader needs a broker or a brokerage company. A trading platform is the tool through which traders can access all necessary information and execute trades.
Trading platforms perform the following crucial functions:
- Information resource. This includes quotes, news, analytics, and other data.
- Market analysis. Trading platforms include tools for technical analysis, helping traders assess market conditions and make decisions regarding position openings.
- Trade management. This involves opening and closing positions, setting protective orders, and more.
- Account management. Traders can open various types of accounts, including demo accounts, and use them for trading and analysis.
- Strategy testing. Many platforms have built-in testers to conduct tests of trading strategies or automated trading programs.
- Trade analysis. Historical trade data can be used to generate reports and evaluate trading performance.
So, how do you pick a good platform? There are several criteria to consider:
- Functionality. Check that the platform has all the necessary tools for market analysis and trading, access to various timeframes, and chart display options.
- User-friendly interface. The interface should be intuitive, even for novice users.
- Comfort in use. This means a clean design, absence of distracting information, and having everything you need readily accessible.
When choosing a trading platform, consider the different versions available:
- A desktop version is downloadable on your computer and accessible only from that device.
- A web platform is accessible from any device with an internet connection.
- A mobile version is intended for use on smartphones.
Modern trading platforms are frequently designed in multiple versions, allowing you to trade conveniently from anywhere and at any time.
How demo account differs from live account
As mentioned earlier, after completing training and certain subsequent preparation stages, it is not recommended to start trading on a live account right away. Instead, it's better to practice first on a demo account.
A demo account allows beginners to gain practical skills and allows experienced users to refine new strategies. So, what are the similarities and differences between these two types of accounts? Let's explore this in this section.
The key difference between a demo account and a live one is that in the former, trading is carried out with virtual funds, while in the latter, it involves real money. Trading on a demo account is like a simulator of real trading.
Another difference is that you can open a demo account without registration with a broker. You can simply download the trading platform and open an account immediately. To open a live account, you must go through a registration procedure.
Additionally, there's no need to fund a demo account. As soon as you open it, it comes with a certain starting capital that you can use for trading.
In all other aspects, the trading process and the ability to open and close positions on a demo account are no different from those on a live one. You can use the same trading assets, analytical tools, and quotes.
How long you use a demo account is a personal choice, as there are no specific limitations. However, it's important to understand that using a demo account for an excessively long period may lead to risk aversion.
Therefore, experienced users recommend using a demo account for no more than one month. Typically, this is sufficient time to gain practical experience, work on trading fundamentals, and acquire all the necessary skills.
What is trader-hamster
When we talk about trading and traders, there are several concepts that you should be familiar with. One of these concepts is who "hamsters" are in a financial market. Let's try to understand this.
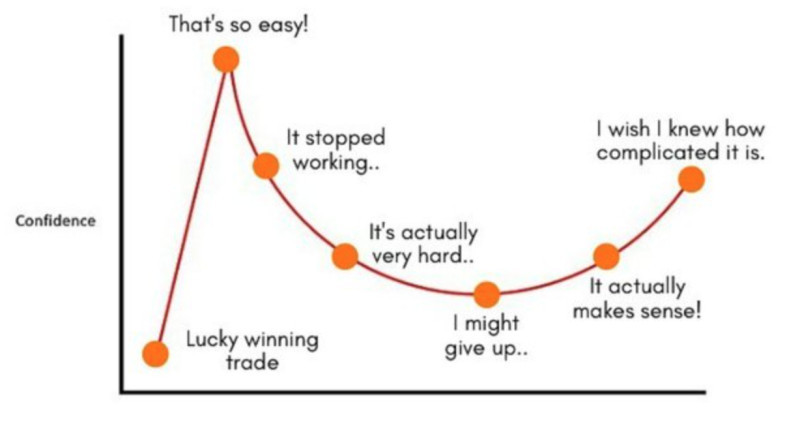
So, hamsters are referred to as inexperienced or novice traders who make hasty decisions influenced by emotions or panic. The distinguishing traits of such users include:
• Opening long positions when the price reaches its peak and short positions when it reaches its bottom.
• The absence of any trading strategy, or if they have one, they often deviate from its rules.
• The desire to achieve high returns without putting in any effort.
• Opening positions based on rumors or unverified information from the Internet.
• Following the crowd and falling victim to scams.
Hamsters in their activities often find themselves pitted against large players known as sharks. These sharks are well-versed in market manipulation techniques and can use them to profit from inexperienced market participants.
For novice traders, the journey is always challenging, but if you follow all the steps we've discussed above, you can avoid becoming a hamster. By undergoing proper education, choosing the right trading strategies and assets, and carefully selecting a broker and trading platform, you can minimize mistakes.
It's crucial to conduct in-depth analysis and market assessment before opening any positions. Besides, it makes sense to diversify a portfolio. While we typically associate this term with long-term investors and asset allocation, diversification is equally relevant in the realm of trading. You can try trading assets from different industries and in different markets to reduce risk.
What is market shark
Now that we've been introduced to various trading slang terms, let's explore another one. In addition to bulls, bears, and hamsters we talked about earlier, financial markets also have sharks.
These players profit by manipulating the actions of other market participants. Of course, only large players who can influence events in financial markets can manage this.
The traps set by sharks are where hamsters and other retail traders fall prey, becoming the source of profit for these major players. To recognize such traps, you need to be extremely vigilant.
For example, if there's information about suspicious contracts being made or transactions involving the same amount of a certain asset within one trading day, these could be signs of manipulation, which should be monitored by market regulators.
Manipulating public opinion is currently one of the easiest methods. Spreading news about a particular company, rumors, alleged insider information – all of these can influence assets’ market quotes, especially valuable securities.
Furthermore, major players can create trends and steer them in their preferable direction. This way, they stimulate specific behavior among other traders who enter the market following the established trend.

There are several main types of market manipulation:
- Collusive trades. Large players engage in transactions with each other, causing changes in the value of certain assets.
- Insider trading means having access to information not yet available to the public and using it for trading.
- Pump and dump means acquiring assets in small portions and then swiftly dumping them, leading to a significant decrease in value.
- Flash crash is a rapid and powerful forced decrease in value. Subsequently, retail traders panic-sell their assets and the sharks profit from this situation.
Experienced what is a trader
There's another category of players in financial markets known as “wolves”. These are experienced traders who have been trading for many years and have executed a large number of trades. Moreover, they possess a wealth of theoretical and practical knowledge about trading.
However, it's important to understand that being an experienced trader doesn't always equate to being wealthy. Generating significant profits in trading is associated with high risk and often requires solid initial investments. Not all market participants have the means or willingness to enter into such conditions. As mentioned earlier, individuals with certain temperaments are not capable of trading but they can develop effective strategies based on their knowledge and experience.
Experience is not just about the number of years spent in financial markets. It implies a deep understanding of the processes happening in the market and the ability to analyze them and forecast future developments.
Every savvy trader should have a personal trading strategy and adhere to its rules in any situation. However, this doesn't mean the strategy cannot be modified or improved. On the contrary, the strategy has to be fine-tuned.
Another crucial aspect is having a clear trading plan, which includes entry and exit points, trade volumes, and the placement of protective orders. Many traders believe that the ability to limit losses differentiates an experienced trader from a beginner.
Moreover, an important trait of experienced traders is the ability to control their emotions and not give in to their influence while trading. Not every trade will be profitable, but there's no need to get into a panic immediately and attempt to compensate for the incurred loss right away.
Earning extra income
When a trader gains enough experience in financial markets, they can look forward to earning extra income through a special tool known as copy trading.
The essence of this service is that a market participant can select one or more successful traders from a list whose positions they would like to replicate in their own account. After subscribing, the selected positions will be automatically duplicated in the trader's account.
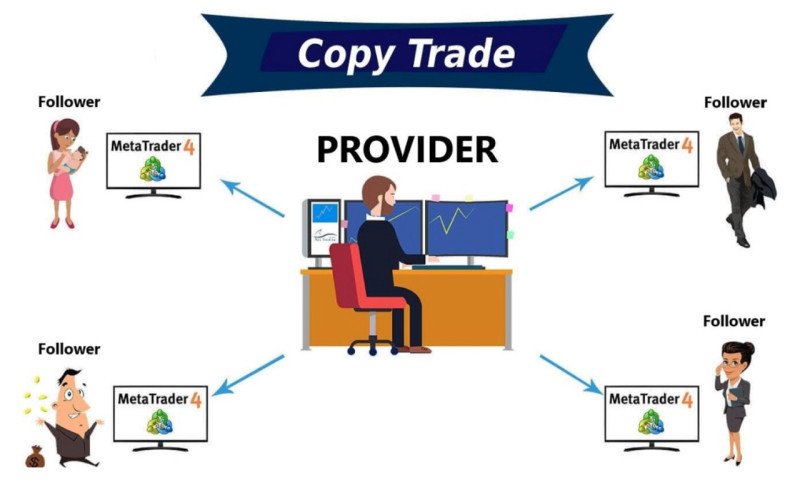
This service is beneficial for both experienced and novice participants. For a savvy trader, it gives an opportunity to earn passive income in the form of a commission for each trade. This commission typically ranges from 10% to 30%.
For beginners, there are several advantages: the ability to generate profit without prior training and independent trading, the opportunity to monitor the positions of experienced traders and learn from them, and the ability to set an acceptable risk level.
However, it's essential to understand that this service entails certain risks for novice users. Since all trades, including losing ones, are copied from the managing trader's account, beginners should be very careful when selecting a trader to copy. It's crucial to pay attention to how long the trader has been active in the market, their track record of past trades, and so on.
Besides, users should monitor whether their account's capital is expanding over time. If the capital isn't growing by approximately 2% per month, it makes sense to change the provider trader's account.
Conclusion
In this article, we have covered key aspects related to trading in financial markets. To become a trader, one needs to follow several essential steps.
First, it is necessary to determine your trading profile and undergo training. Self-study is an option, with numerous articles and books available for free. Additionally, there are various online and offline courses that can be acquired for a fee. Some brokers offer free training upon account registration.
Next, one should select a brokerage company and a trading platform. A broker serves as an intermediary, enabling retail traders to enter financial markets. A trading platform is where trading takes place, where quotes are tracked, and where analysis can be conducted.
Another crucial requirement is the development of a personal trading strategy. Initially, this might be challenging, but with experience, it will be inevitably invented. It is essential to align the strategy with one's character and temperament type and strictly adhere to its rules in all situations. While it doesn't guarantee that all trades will be profitable, it ensures a positive overall balance.
Furthermore, an experienced trader with a solid trading strategy may earn additional income by having their trades copied by novice users.
Lastly, another essential requirement is practicing on a demo account before depositing an account with real money. This enables a beginner to gain practical experience and understanding of how the market operates, how trades are executed, and all other specifics.









 Back to articles
Back to articles














