
No trader can directly speculate in the markets. Every trader vs broker requires an intermediary through which they can access financial markets and carry out all trading operations.
Brokerage companies act as such intermediaries. They actually execute orders placed by traders. In this article, we will talk in more detail about their functions, specifics of their operation, advantages, and disadvantages.
You can learn more about who traders are and how to become one, what basic steps have to be taken for this, as well as what categories of traders there are and how to choose the most suitable one for yourself, from the article What is a trader.
What is broker vs broker
A broker is a professional intermediary between any trading participant and the market. Intermediaries can be both individuals and organizations. They provide clients with access to markets and the opportunity to make transactions on them.
Not only specialized companies, but also investment, banking, and some other organizations act as brokers.
In most countries of the world, this activity is subject to government regulation and mandatory licensing. Therefore, to engage in such activities, a special permit is required. In addition, different states put forward additional requirements, such as a minimum authorized capital and some others.
Such requirements encourage the improvement of the quality of services provided and prevent the use of fraudulent schemes. Nevertheless, you may encounter unscrupulous intermediaries in the market, so you need to be careful when choosing a broker.
In essence, an intermediary’s work is to carry out transactions in the market on behalf of its clients. For this reason, in order to avoid conflicts of interest, they are prohibited from trading on their own behalf and holding open positions in shares or other assets.
For their work, brokerage companies receive payment in the form of a commission, which is charged for each transaction. It can be fixed or floating. Commonly, a commission is set as a certain percentage of the transaction amount.
Larger companies can also make money through margin trading. That is, they lend money, shares, or other assets to their clients and earn money in the form of interest.
Broker’s functions
Brokerage companies exist not only in financial markets. They also operate in the insurance, credit and leasing sectors, the real estate market, cargo transportation, and some other areas.
At the same time, to carry out activities in each individual area, it is necessary to select a specialization and obtain an appropriate license from the regulatory agency.
As for brokerage companies working in trading and investment, their main function and role is moderation in transactions. Thanks to their activities, traders can enter the markets and trade.
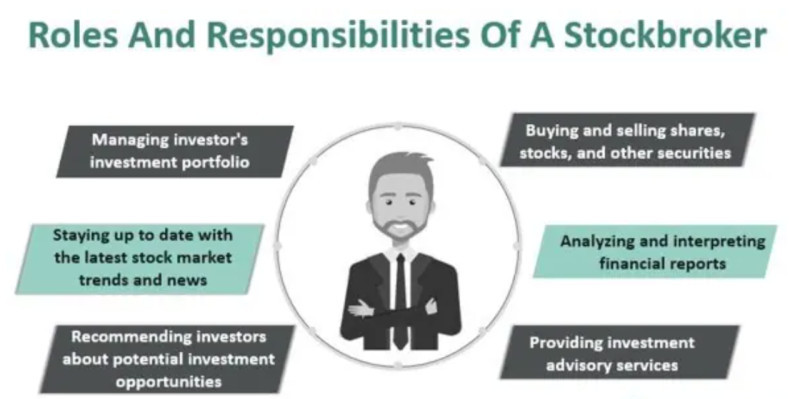
However, this is not their only function. In addition to the role of intermediary, brokers also perform other actions:
• Monitoring the financial situation in the markets;
• Storing money, shares, and other assets;
• Risk insurance and liability in case of losses;
• Carrying out analysis of completed transactions;
• Daily statistics on operations;
• Development of trade and investment strategies;
• Maintaining documentation and, in some cases, filing tax returns for traders;
• Conducting workshops and training for traders;
• Providing analytical reviews and market news.
In addition, some intermediaries develop and offer services using their own trading software, trading platforms. In such a situation, you don’t have to resort to the services of third-party software developers.
All these extra services are provided with one main goal - to attract more users. After all, the more traders become clients of a brokerage company, the more funds it can receive from them in the form of commissions on transactions.
Types of brokers
Most market participants have probably heard terms such as ECN, STP, NDD, and others, but not everyone knows what these abbreviations mean. Let's take a closer look at what is hidden behind these symbols and what is the difference between them.
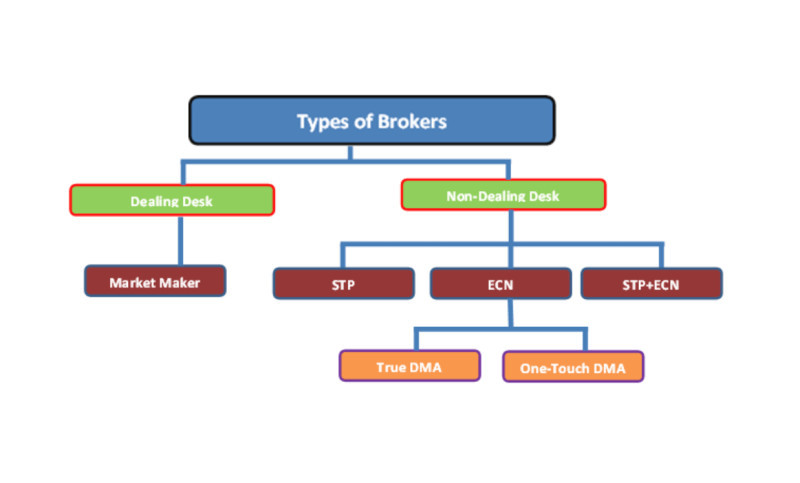
These abbreviations are responsible for the types of order execution. Depending on the type used, intermediaries are divided into:
• DD (Dealing Desk) involves conducting transactions through a dealing center. These include the so-called market makers, who manage the main flows of quotes and are key providers of liquidity. They bring together requests from sellers and buyers.
NDDs are intermediaries who do not use the services of a dealing center. They use other technologies to execute orders:
- STP is an automated technology that works without the use of a market maker. Such intermediaries have their own liquidity pool, which is represented by different providers and makes it possible to execute orders at the best possible price.
- ECN is an electronic technology that gives a trader the opportunity to enter the market without intermediaries. In this case, the broker acts as the only liquidity provider.
• STP/ECN is a mixed model that combines the best elements of the two above technologies. It allows traders to fully automate the process of placing and executing orders, without the need to resort to the services of market makers.
As mentioned earlier, intermediaries exist not only in the area of trading in financial markets, but also in other areas. Accordingly, depending on the type of activity, the following brokers are distinguished:
- Stock brokers are intermediaries who buy/sell shares on the stock exchange, enabling the participation of both retail investors and companies in trading;
- Insurance brokers offer insurance services in any location, select the most optimal options for each individual case;
- Customs brokers provide assistance in customs clearance. They are intermediaries between customs authorities and clients;
- Credit brokers offer lending services and provide advice and all the necessary information on this topic
- Real estate brokers provide assistance in making contracts for the purchase or lease of commercial and other premises.
How to pick a broker
Selecting an intermediary company is an important move on the path to becoming a trader. This does not mean that you need to choose one mediator for life. During the trading career, a trader may revise strategies, priorities, and needs. Accordingly, the requirements for a broker may also change.
However, there are a number of criteria that must be taken into account when choosing a brokerage company at any stage of your activity as a trader. Let's take a closer look at what these criteria are and why they are important.
1. Regulation. In general, the activities of intermediary companies are quite strictly regulated by the relevant authorities in each individual country. A reliable broker must have a license or any other permit provided in the country of its registration to carry out activities.
2. Reliability. This category includes experience and duration of work, the reputation of the company among market participants, user reviews about cooperation with the company.
3. Tools. It is necessary to pay attention to the number of trading instruments that the intermediary provides for trading. Moreover, when choosing specific tools, you need to look for a leader in this area.
4. Order execution. This point is of paramount importance for those who practice short-term strategies, especially scalping. Indeed, high speed of transactions is a key criterion for achieving success.
5. Types of accounts and initial deposit. An important point especially for novice users is the ability to open different types of accounts, including a demo account or cent account. In this case, you can start trading with a minimum deposit.
6. Commissions. Each brokerage company charges fees for the services provided. In some cases, these are fixed amounts, in others, they are floating depending on the amount of the transaction. It is necessary to choose the option that is optimally suited for a specific strategy and trading style.
7. Deposit/withdrawal options. Different companies have different options and terms for replenishing an account and withdrawing money from it. Please take notice of these terms and conditions.
8. Customer support. An important criterion is the availability of support service in the trader’s language. Besides, this item includes any additional services: analytical reviews, training opportunities, comfort when working with a broker, etc.
How trader and broker interact
So, after the trader vs broker has managed to choose “that particular” broker that most ideally fits all criteria, it is necessary to have a clear interaction algorithm.
- The first thing you need to do is make an agreement. Before this, it is necessary to study all the conditions and carefully read the public offer agreement. On the basis of this document, certain obligations arise between the trader and the broker. Currently, contracts can be finalized remotely.
- Open a live account and top it up with real money. Using a demo account, as a rule, does not entail any obligations. You can use it even without registration. Opening a live account is a more serious and responsible step.
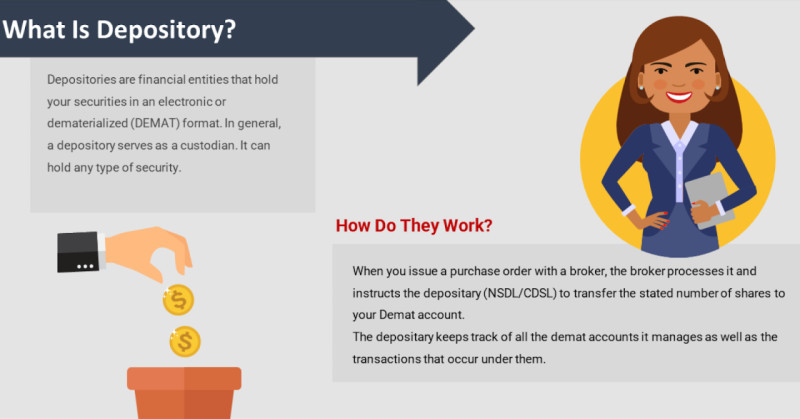
3. When purchasing securities, you will need another account - a depository account. Securities are held in this account. Sometimes you have to look for depositories separately, but oftentimes, brokerage companies themselves have permission to engage in such activities.
4. Start trading. When all the necessary preparatory steps have been completed, you can proceed directly to trading. Orders to buy or sell assets can be made in any convenient way: by phone or online through a special trading terminal or smartphone application.
5. The broker, in turn, executes orders placed by the trader, for which the intermediary receives fees. The commission amount is debited from the brokerage account along with the asset’s amount.
6. The profit received as a result of successful transactions can be transferred from the brokerage account to your bank account. However, there may also be some fees related to this.
7. Payment of taxes. According to the legislation in a number of countries, the broker has an obligation to calculate and withhold tax on the income received by the trader. The percentage rate at which tax is calculated may vary from country to country.
How trader and broker differ
A trader and a broker are a tandem for effective work in any financial market. Just as the first cannot trade without the second, so the second cannot exist without the first.
Many users confuse traders and brokers, although their functions and roles in trading are very different. The key difference is that the trader places orders to buy or sell assets, and the brokerage firm executes them.
Speculators trade in financial markets. However, they cannot carry out their activities directly. Between the trader and the market, there is a mediator, i.e. a broker who directly transmits the user’s orders to the market.
Another point that could cause confusion is that traders do not always trade on their own behalf, they can make transactions on behalf of third parties. But even in such a situation, orders are still executed by an intermediary company.
Another distinctive point is that the trader makes a profit only in case of a successful transaction. The broker receives its commission regardless of the user’s trading results.
Importantly, the intermediary carries out transactions on behalf of the client and in their interests, at its own risk. Unlike the trader, the brokerage company does not bear the risk of losing its own funds when executing orders.
There are other market participants who are often confused with traders, but they perform completely different roles. For example, a stockbroker performs similar functions to a broker, but the specifics of this work are somewhat different.

Stock brokers, as the name suggests, work primarily on stock exchanges and are also intermediaries in securities transactions. At the same time, brokers carry out transactions based on traders’ requests, but on their own behalf.
A dealer or dealing center is also an intermediary, but unlike a broker, it executes orders on its own behalf and at its own expense. Thus, the dealer risks its own funds, not the client's money.
How to become broker
In colloquial speech, brokerage companies are often called brokers. However, this word can be used in another sense, directly designating a person who is an employee of an intermediary company and provides relevant services.
A broker is the same profession as a trader. They can work not only in specialized brokerage companies, but also in other financial organizations: banks, investment funds, and other firms. Some brokers work individually, but this is quite difficult.
In order to work as a broker, you need to have an education in the field of finance, but specialists with technical education can also work in this area. Important qualities for brokers are speed of reaction and the ability to work with a large amount of information.
Also, one of the most important skills is communication as brokers have to constantly communicate with a large number of people. You must have an analytical mind, planning, and forecasting skills for various situations.
Apart from training, large companies also require internships. An additional bonus of an internship in large companies is that if it is successfully completed, the specialist may be offered employment in this company.
This type of activity is licensed in most countries, so you will need to obtain a license, undergo certification or obtain any other type of accreditation (depending on the requirements of a particular state).
The list of responsibilities of this specialist includes:
• Buying/selling goods, securities, currencies, and other assets on exchanges;
• Establishing business contacts between the parties to the transaction;
• Selection of the best offers and the most favorable conditions for the transaction;
• Preparation of all necessary documentation;
• Carrying out analysis of completed transactions and settlements;
• Providing advice to clients.
What is prime broker
Primary brokers are the largest liquidity providers. This category includes organizations in the banking and investment sectors that enable market participants to enter financial markets.
Such companies do not work directly with retail traders. They provide a range of services to smaller intermediary companies, hedge funds, and other organizations that work with individual traders.
Among the most important services provided by prime brokers to their clients are: clearing, operational services, support for mutual settlements, risk and money management.
Primary brokers are a key link in trading on the foreign exchange markets for traders around the world, as they provide:
The best conditions for trading (small commissions, maximum leverage, number of quotes and margin requirements;
• Liquidity of transactions in various markets, including Forex, commodity, stock, and others;
• Technical capabilities for receiving quotes from several trading platforms at once;
• Opportunities for withdrawing gains even from cent accounts.
Only prime brokers have access to the interbank market, so they are the ones who execute trades on behalf of smaller companies. The most well-known prime brokers are Morgan Stanley, Bank Of America, JPMorgan Chase, Deutsche Bank, and some others.
Since 2008, when the global financial crisis occurred, the requirements for prime brokers have been tightened. Thus, collateral requirements were ratcheted up 3 times, leverage was reduced and monitoring requirements were upgraded.
Pros and cons of working via broker
Despite the fact that it is impossible for retail traders to enter the markets without an intermediary, the interaction between a trader vs broker has both its positive and negative sides. Let's consider them in more detail in this section.
So, the advantages of working with a brokerage company include:
- The broker provides software for trading, including access to the trading platform, and mobile application;
• The trader does not have to prepare, generate reports and other documents, and file returns with tax authorities on their own;
• The broker provides analytical reviews, economic calendar, and other resources;
• Training opportunities are also available as many brokers offer free training if a client opens an account with them, which saves time and money;
• The broker offers a large number of trading instruments, so you can choose exactly those to suit your needs;
• The broker arranges various ways to replenish your account and withdraw funds from your trading account;
• The broker has affiliate programs and holds competitions and promotions to provide clients with additional benefits such as the opportunity to win a valuable prize or receive interest from transactions of clients attracted through the affiliate program.
At the same time, cooperation with brokers also has a number of disadvantages:
- Commissions are charges. Apart from commissions for transactions (spreads), which are specified in the contract, brokers also have hidden commissions. For example, a swap is a fee for maintaning an overnight position, interest for margin trading, commission for withdrawal of funds and some others;
• Income is not guaranteed. Each broker warns in the contract and on its website that trading and the potential for profit entail the risk of losses. The broker cannot influence quotes and ensure that the trader receives income;
• Fraudulent schemes. Often in the markets you can encounter unscrupulous brokers who try to defraud traders of their money and do not provide any services in return;
• In case of bankruptcy of a broker, difficulties may arise with the return of funds. Securities are kept in a separate account, but money may disappear.
Conclusion
In this article, we looked at what a broker is, what types of brokers there are, and what their main functions are. The tandem of a trader and a broker works inextricably since one cannot function without the other.
In order to avoid disappointments in the future, you need to carefully consider the choice of s brokerage firm. This type of activity is licensed in most countries of the world. Therefore, a broker has to obtain a special permit.
In addition to the intermediary function directly in concluding transactions in financial markets, such companies also carry out a number of other activities: consulting and training clients, preparing reports and documents, developing trading strategies, and others.
Brokerage companies receive a fee for their services: commissions. In most cases, these fees are charged for each transaction made by the client, either as a fixed amount or as a percentage of the transaction amount.
On top of that, brokers may charge hidden fees for rolling over an open transaction to the next day, for withdrawing funds from an account, and some other fees.
When selecting a broker, you need to pay attention to other points: trading instruments, experience in the market, types of accounts, speed of order execution, and other criteria.
You may also like:








 Back to articles
Back to articles















