
New blockchain networks and their related cryptocurrencies are entering the market almost daily. However, not all of these projects achieve success. Some fail to stay afloat even for a year. This is because attracting investors and drawing attention to one's project requires developers to present something truly new and unique that stands out from what's already available in the market. This article will discuss one such unique and promising project – the Fantom platform.
To learn more about other digital currencies that are in the top 100 cryptocurrency rankings, as well as how these rankings are compiled and how to use them correctly, one can refer to the article Cryptocurrencies list.
What is blockchain and how it operates
Blockchain is a network where all transactions made within it are recorded in a special decentralized ledger. To better understand what blockchain is and how it works, let's examine its main characteristics:
- A decentralized ledger means that data is stored simultaneously on multiple devices or servers around the world, which are independent of each other.
- A system of blocks, into which transaction records are entered. Blocks are linked sequentially to each other, making it impossible to alter any record in any block without changing the rest of the blocks.
- Cryptographic protection. All data is encrypted using a special technology. Only the person with a special key can decrypt it.
Let's briefly look at the blockchain operation process and how a record is entered into it. When a user initiates a transaction, such as sending several digital coins to another user, a record of this transaction appears in the blockchain.
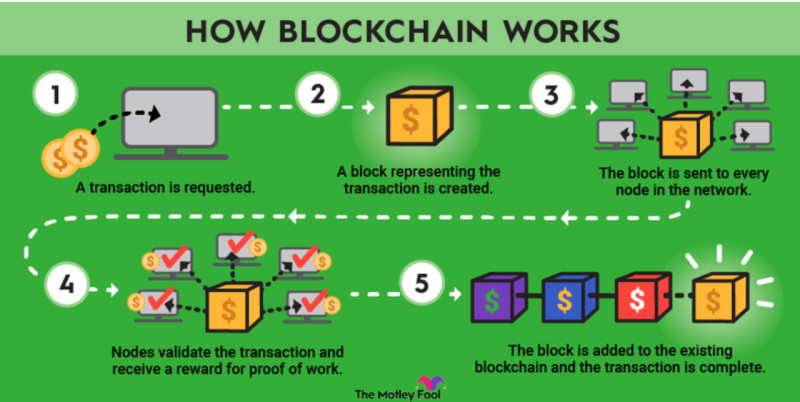
Next, the system checks whether the user has the necessary amount in their account. If so, the money is transferred to the recipient, and the transaction is recorded in a network block. Blocks are linked together in a chain, thus forming a blockchain.
We've already mentioned that blockchain is characterized by decentralization, but data about the new record is synchronized across all network devices. For this, the network has a consensus algorithm that allows all remote devices to coordinate and contain the same information.
Data protection is ensured through cryptographic encryption. Typically, two keys are used in cryptocurrency networks: a public and a private key. The former encrypts data and can be verified by other network users for authenticity. However, data can only be decrypted using the private key.
Main blockchain issues
Many blockchains, especially those developed in the early stages of digital currencies, face several main problems in their operation.
The three main issues these networks encounter are:
- Transaction processing speed within the network;
- Network scalability;
- Maintaining decentralization and security.

To determine the speed of operations, there is a special parameter – the number of transactions per second (TPS). For many networks, as the number of operations increases, so does the time it takes to conduct each one. This parameter becomes the key in evaluating the efficiency and utility of a blockchain.
The first networks to appear, such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, cannot boast high values of this parameter: Bitcoin's TPS is 3-7, while Ethereum's is 15-25. Meanwhile, many modern blockchains can process from 1,000 to several thousand transactions per second.
The next issue is scalability, which is closely related to the speed of processing operations. Scalability allows for the expansion of the network, meaning it can serve a greater number of participants and, accordingly, handle more operations.
As the number of nodes in the network increases, so does the time required to process an operation. Consequently, networks struggle with a large number of transactions, resulting in a queue of unprocessed operations. New blockchains find alternative solutions to this problem through new consensus mechanisms.
With the increase in the number of devices involved in the blockchain, the level of decentralization increases. However, as mentioned, its throughput decreases. How these issues are addressed by various modern networks will be examined using the Fantom platform as an example.
FTM in essence
FTM refers to Fantom, the name of a decentralized network. On one hand, it is one of the many blockchains currently in existence, with several thousand available. On the other hand, it possesses certain features that set it apart from other similar platforms.
Various modern blockchains focus on different network characteristics. Some aim to increase speed and TPS, others try to attract users by reducing transaction fees, while others promise enhanced security, and so on.
So, what distinguishes Fantom from other similar projects, and what makes it unique? Fantom is a network that allows the development of decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts. However, this network has a somewhat different structure or distributed ledger technology, called DAG.
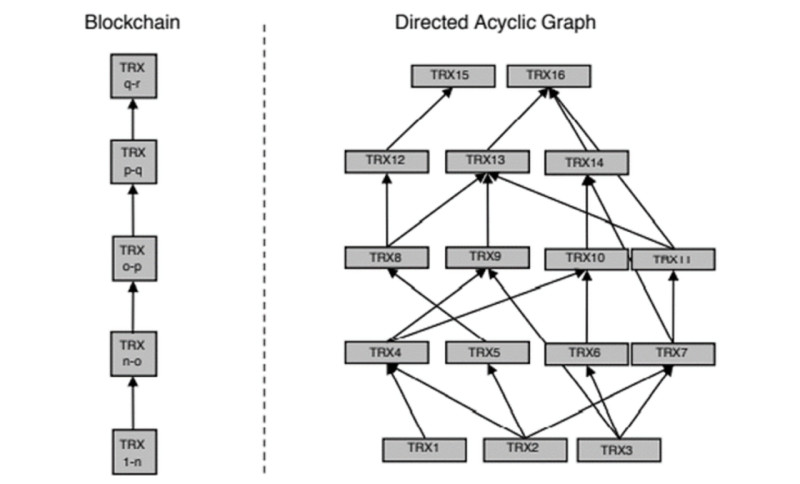
In blockchain technology, blocks are sequentially linked together. In a DAG-based network, data is not grouped into blocks. Therefore, there is no need to record it in any specific sequence. This, in turn, opens up new possibilities for scaling the network.
Additionally, the network utilizes a special consensus algorithm – Lachesis aBFT, which is a variant of PoS. This enables transactions to be processed in fractions of a second, allowing the TPS for this platform to reach up to 4,500.
The developers have also launched a virtual machine compatible with the Ethereum network and other well-known networks. This means that Ethereum developers can use this network to launch their projects due to the ease of migration. At the same time, the Fantom platform offers broader possibilities for application development.
History of FTM invention
The platform originated in early 2018 in South Korea, created by a Korean already known in his country for other projects, such as the restaurant rating app SikSin. Subsequently, the project changed its location and leadership team.
In its first six months, the company attracted investments from venture capital funds to finance the project, and by mid-year, it conducted a public sale of the company's tokens in an ICO format.
The company positioned itself as the world's first smart contract platform based on DAG technology, which simultaneously addresses the issues of network scalability and transaction speed. The project is intended for implementation in various sectors: food service, logistics, finance, and others.
Through venture capital funding and the ICO, the company sold about 40% of the network tokens and raised nearly 40 million US dollars. Meanwhile, the platform continues to grow, its currency is considered one of the fastest-growing, and its capitalization now exceeds 1 billion dollars.
The team constantly works on improving existing options and adding new features to increase the network's performance and efficiency. Besides, the network keeps expanding and attracting more users, contributing to its further popularization.
A year later, the developers launched the Opera network, which currently serves as the main network for Fantom. It is open-source, and it's where decentralized applications are hosted. This network also circulates its native token, FTM, which we will discuss further.
Native token FTM
The FTM cryptocurrency is the utility token of the Fantom network, used for various purposes. Its main function is to support the operation and security of the network.
This coin is issued in several forms for use on different platforms:
- Opera FTM – for the Opera network itself;
- ERC-20 FTM – for the Ethereum network;
- BEP-2 FTM – for the Binance Chain.
As mentioned, one of the key purposes of the FTM token is to ensure the security and operation of the platform's consensus mechanism. To become a validator in the Fantom network, one must hold at least 3.175 million utility tokens.
Accordingly, the more currency units a user holds, the greater their voting power becomes. Therefore, validators act in the community's interest, encouraging other users to delegate their tokens through the staking process or to receive rewards for a new block.
Another important function of the FTM token is to pay for transaction fees within the network. The fee amount directly correlates with network congestion: the higher the load, the higher the fees. Thus, this rate can fluctuate from $0.01 to $0.1, but often it amounts to fractions of a cent.
The price of one token at the time of writing this article is about $0.35, making it quite affordable. The total maximum supply of this currency is 3.17 billion units, with about 2.8 billion in circulation. The remaining tokens are locked for staking rewards and other purposes.
How Fantom Works
The Fantom platform, as previously mentioned, has several distinguishing features that set it apart from other blockchains. Let's delve into what FTM is and how this network operates.
What sets Fantom apart from other similar networks is its unique "leaderless" consensus algorithm, Lachesis, which allows multiple transactions within the network to be verified simultaneously and independently. Subsequently, individual operations are collected into blocks, which are then interconnected.
This differs from linear blockchains, where individual nodes send blocks to each other for verification and agreement. In Fantom, validators periodically exchange data and synchronize it with each other, typically within a few minutes.
The platform's structure comprises three levels that ensure its operation. The first level is the base, which facilitates consensus among all nodes. The second is an intermediate level designed for payments and rewards. The third is the application level, intended for hosting APIs and dApps.
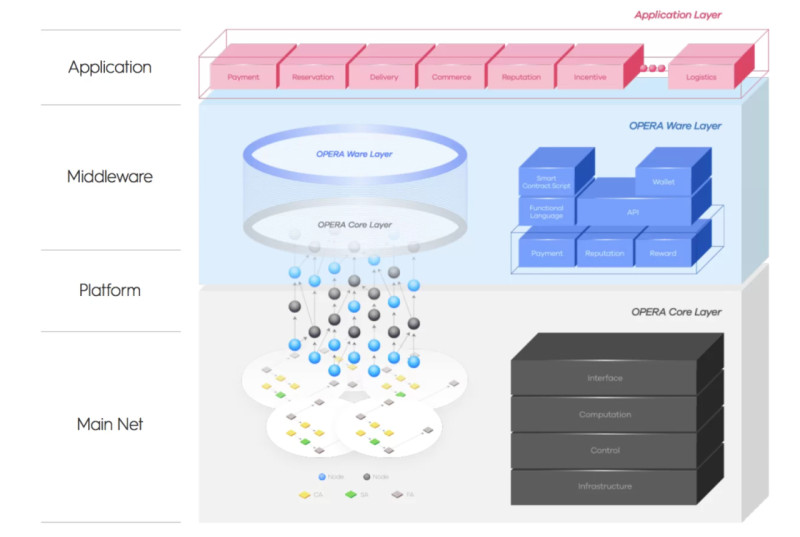
This multilevel structure allows the platform to be more flexible. Fantom is essentially a network of networks, enabling these autonomous networks to support the operation of several decentralized applications without overloading the platform itself.
Regarding application development, the platform offers a modular system containing various blocks. This modularity allows developers to choose exactly the tools and components they need, significantly simplifying the creation and implementation of applications.
Key features
As has been repeatedly mentioned, the Fantom platform possesses several distinctive characteristics that set it apart from other similar networks. Let's delve into these key features and the advantages they offer.
One of the key features is the ability to conduct multiple transactions simultaneously. This is made possible because operations are verified by different nodes, which then exchange data and synchronize the information.
This becomes feasible thanks to a unique consensus mechanism that does not require blocks to be sequentially linked. This is where the platform differs from many others: here, a larger number of nodes accelerates the network's operation, whereas in a linear blockchain structure, it slows it down.
Therefore, the platform aims to attract more validators, while its number of nodes in the network is still relatively small, totaling only 58 compared to other networks where their number runs into thousands. The high entry threshold was a barrier, but the company is already working in this direction and has decided to lower the threshold to 50,000 FTM.
Another feature is that holders of the platform's native tokens have a say in the company's governance. They can propose their ideas for improving services and vote on all updates. The focus is on building and developing a community of like-minded individuals who will jointly manage the network.
Another characteristic of this platform is its compatibility with other networks, such as Ethereum and Cosmos. This allows developers to use all available functionalities to launch new products, significantly reducing costs.
One of the features that distinguish the FTM cryptocurrency from many other digital currencies is that it cannot be mined. This means the coin cannot be obtained through mining, but it can be purchased on all known centralized and decentralized cryptocurrency exchanges.
Fantom cryptocurrency: pros and cons
We have already discussed FTM, which is not only a cryptocurrency but also a fairly large platform for conducting various operations. Now, let's consider the advantages and disadvantages of this network.
The main positive characteristics of Fantom include:
- High performance. As mentioned, this network significantly outperforms many others, even more famous and popular networks such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, in terms of the number of operations processed per second.
- Low fees. The size of the fees depends on network congestion, but thanks to the technologies applied on the Fantom platform, overloads are almost impossible. Hence, the transaction fees are record low, attracting a large number of users.
- Token availability. FTM coins are traded on a large number of exchanges, both centralized and decentralized, making transactions straightforward. Additionally, the token's cost is relatively low, making it highly accessible.
- Incentivization. The platform directs its efforts not only to encourage users but also to reward developers. This approach is aimed at long-term prospects and creating a more sustainable community.
Among the key disadvantages are the following:
- Significant initial capital is required to operate as a validator. Launching your own node in this network requires a large number of FTM tokens, which, even considering the token's low cost, amounts to a substantial sum. However, the team is already working on lowering the entry barrier.
- High market competition. New cryptocurrencies and their associated blockchain networks emerge almost daily, and the Fantom platform faces stiff competition. Therefore, it's necessary to continually work on the quality of services provided to maintain an advantage.
- Limitations in application in "Smart City" systems. Projects such as "Smart City" or "Internet of Things" are still only beginning to develop, and the Fantom platform targets these projects. However, its practical use in these areas is not yet feasible.
Fantom's prospects
Having discussed the Fantom platform and identified FTM as a unique network with several distinctive characteristics, what potential does this network have? How might it develop?
The main direction of this project's work, as mentioned, is decentralized finance and decentralized applications. The platform offers opportunities for application development in a wide range of fields: financial, social, and many others.
Additionally, the platform continuously enters partnerships with other major projects, which allows it to expand its capabilities and sphere of influence. One of the most attractive directions for the Fantom platform team is attracting partners for integration with business and government administration.
The project team's goal is to go beyond the blockchain network and change something in the real world, not just the virtual one. This primarily concerns creating infrastructure for areas requiring secure storage of large data volumes and high-speed data processing.
The Fantom team has developments that can be applied in healthcare, document management, education, utility services, traffic management, and some other areas.
One of the main and most interesting projects is creating infrastructure for "Smart City". This implies connectivity between various systems and sectors within a single city, process automation, quick identification and resolution of issues, and so on.
Starting in 2021, the platform launched a grant program to attract and stimulate developers. The first grants were allocated a total of 370 million FTM tokens, amounting to about $300 million, with the total sum of locked funds currently exceeding $10 billion.
The Fantom project is still at the beginning of its development, but if its creators manage to implement all their ideas, it could achieve tremendous success. Additionally, the company plans to reach an even higher TPS level of 300,000 in the future (currently, the network's rate is 4,500).
Conclusion
In this article, we have explored questions such as what the FTM platform and its native cryptocurrency are, what unique features it possesses, and its advantages and disadvantages.
The developers of the Fantom platform attempted to solve several major issues that nearly all blockchain networks face: scalability, transaction speed, and maintaining network decentralization and security. In this network, a larger number of nodes contributes to increasing the network's operational speed.
The solution to these problems lies in the platform's unique "leaderless" consensus algorithm called Lachesis. It allows different nodes to independently process multiple transactions, enabling the network to achieve a Transactions Per Second (TPS) rate of 4,500.
This is made possible by the DAG technology, where transactions are not grouped into blocks that are then sequentially linked. In this network, records are made independently of one another, and nodes simply exchange information and synchronize data afterwards.
Thanks to this, the platform can process large volumes of information at high speed. The project is aimed and already has developments for creating infrastructure for the "Smart City" project, which integrates all services and systems to optimize and automate their operations.








 Back to articles
Back to articles

