
Competition within the cryptocurrency market intensifies as digital currencies gain increasing popularity. Yet, to secure your foothold amidst this fervor, offering something genuinely distinctive or exceptional is imperative.
In particular, unique consensus algorithms play a pivotal role in facilitating network scalability and streamlining transaction processing. One such groundbreaking solution is presented by the innovative Cardano platform, the features of which we shall delve into within this article.
For further insight, explore additional currencies within the top 10 rankings by market capitalization, along with opportunities to enhance blockchain operations and advance its technologies, as outlined in the article about cryptocurrencies.
Generations of cryptocurrencies
All digital currencies are intrinsically tied to blockchain technology, a foundational system ensuring the proper functioning of cryptocurrency networks and platforms through meticulously crafted mechanisms.
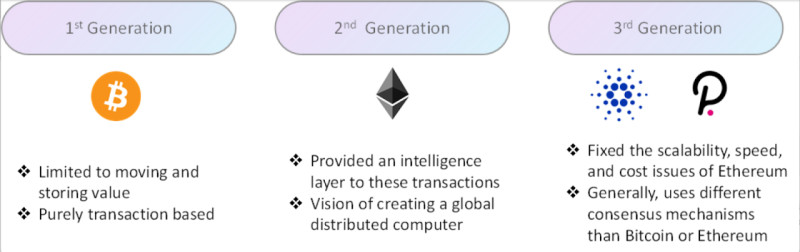
However, akin to any evolving technology, blockchain has undergone and continues to undergo distinct developmental stages known as blockchain generations, of which there are presently three:
- First generation: Networks falling within this category encompass the blockchain of the world's leading cryptocurrency – Bitcoin. This pioneering network emerged as an alternative to the contemporary financial system, affording users the ability to exchange currency sans intermediaries such as banks.
- Second generation: Blockchains at this level, exemplified by Ethereum, expanded beyond currency transfer to encompass the establishment of transaction conditions. Moreover, this stage heralded the advent of smart contracts, automatically executing transactions upon meeting specified conditions.
Simultaneously, the notion of decentralized finance and decentralized applications took root, fostering an environment for their inception with diverse application scenarios.
- Third generation: As user interest in cryptocurrencies and blockchain burgeoned, new challenges surfaced. Existing networks grappled with processing the escalating volume of transactions, resulting in prolonged processing times and escalating transaction fees.
Consequently, emerging platforms embarked on quests to address scalability issues and augment network capacity. These endeavors led to the development of novel consensus mechanisms facilitating expedited operations. Among the vanguard networks pioneering this evolution is Cardano, a focal point of our discussion.
What is Cardano?
So, as we've come to understand, Cardano represents a third-generation blockchain, positioning itself as the most cutting-edge and sophisticated platform currently available. What distinguishes it from the plethora of other projects on the market? Let's delve into its unique features.
The project distinguishes itself through its innovative approach, specializing in decentralized application development and supporting smart contracts—attributes shared by other networks as well.
However, Cardano sets itself apart by tackling the fundamental challenges inherent in blockchain technology. The primary hurdles faced by early blockchains encompass scalability, transaction speed, and the preservation of decentralization and security.
Scalability and transaction speed are intricately linked. First and second-generation networks utilize the PoW (Proof of Work) consensus algorithm, resulting in transaction times ranging from several minutes to several hours. This delay is exacerbated by the burgeoning user base and, consequently, transaction volume.
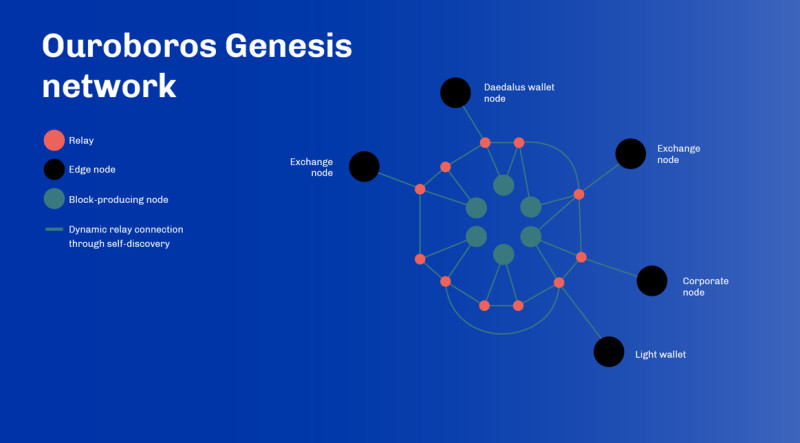
To solve this problem, Cardano has developed its own consensus algorithm, Ouroboros, which is a type of the PoS mechanism. Operations in such networks are controlled by validators, not miners. And they require significantly less energy and time, so that operations are carried out faster and cheaper.
Apart from this, another difficulty that many blockchains face is the inability to interact with other networks due to different codes and technologies. Cardano proposes to solve this problem with the help of an inter-blockchain bridge, which allows using virtual machines to convert information from one network to another.
History of Cardano
The brainchild behind the Cardano network and its native token, the ADA cryptocurrency, is Charles Hoskinson, a co-founder of the Ethereum network. This close association often prompts comparisons between the two blockchains, yet Ethereum falls short in several aspects when juxtaposed with Cardano.
Hoskinson parted ways with another prominent figure in the Ethereum network, Vitalik Buterin, over divergent visions for its future development. Subsequently, he opted to depart from the project, venturing to establish his own, more advanced blockchain.
The inception of Cardano germinated in Hoskinson's mind as early as 2015. Rallying a team of kindred spirits, he co-founded the company IOHK. The fruition of the project followed two years later, with its launch in September 2017, coinciding with the commencement of ADA token trading.
The roadmap for Cardano's evolution comprises five distinct phases:
- Byron – inaugurating the platform and its native currency in 2017.
- Shelley – introduced in 2020, this phase ushered in staking as an option, enhancing network decentralization. The digital currency's capitalization experienced robust growth during this phase.
- Goguen – commenced in 2021, marked by the integration of NFTs and smart contracts—self-executing agreements. Cardano adopts the Marlowe programming language, lauded for its simplicity and user-friendliness compared to Solidity.
- Basho – slated as the fourth phase, focused on bolstering network scalability through the implementation of sidechains. This strategy aims to alleviate strain on the primary network without compromising transaction volume.
- Voltaire – the fifth phase, envisions transitioning the platform to community self-governance. ADA token holders will wield the authority to partake in project management through voting on diverse issues and proposing amendments.
How does Cardano work?
Cardano has a two-layer structure that splits tasks when transferring data:
- Cardano Settlement Layer (CSL) at this level all translations are performed
- Cardano Control Level (CCL) contains all tools necessary for the functioning of smart contracts and apps .
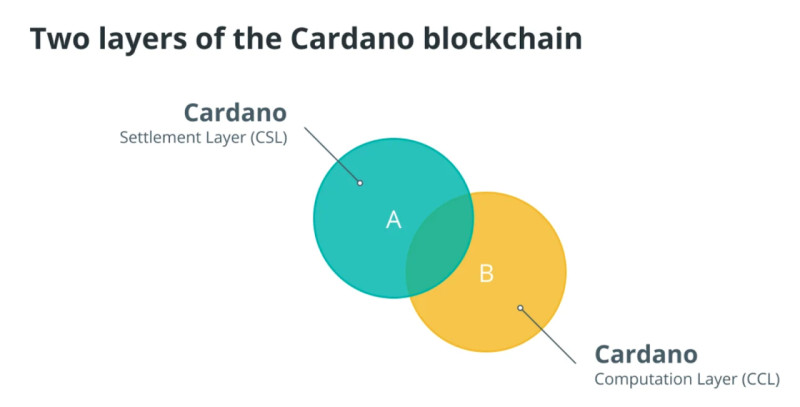
The CSL layer is engineered to facilitate the swift transfer of native ADA tokens while optimizing blockchain velocity. Moreover, it shoulders the responsibility of managing sidechains and interfacing with other networks. Employing a variety of signature types, this layer fortifies security measures.
Conversely, the CCL level is tasked with smart contract development and dApp deployment. Here, developers can craft applications in multiple programming languages, ensuring compatibility with diverse platforms. Additionally, this tier guarantees that data storage complies with legal regulations.
But why segment the blockchain into distinct layers? This segmentation enables individual layers to undergo updates independently, preserving network throughput and bolstering transaction confidentiality.
As previously mentioned, the Cardano platform operates on its proprietary algorithm mechanism – Ouroboros. Developed by a consortium of scientists drawing from cryptographic research conducted across esteemed global universities, this algorithm stands out for its decentralization, eliminating the necessity for a central authority to synchronize the ledger. Transaction verification and block addition to the network are entrusted to ADA token holders, serving as validators.
Notably, this technology operates with minimal energy consumption for transaction processing, underpinned by a mathematical proof of security. This unique approach renders the network simultaneously fast, scalable, and robust.
ADA Token
We have extensively discussed Cardano's native cryptocurrency, ADA, in previous sections. In this segment, let's delve further into this token, starting with an intriguing historical note. ADA derives its name from Augusta Ada King, the daughter of renowned poet George Byron, who gained fame as a mathematician and the pioneer of the first computer.
ADA holds a pivotal role in facilitating the operations of the Cardano platform. The currency serves multiple functions:
- Transaction Commissions: ADA is utilized for paying transaction fees within the Cardano ecosystem.
- Staking: Users can stake tokens to support the system's functionality and, in return, receive rewards, calculated as a percentage of the staked amount.
- Validator Remuneration: Network validators are rewarded with ADA for their role in ensuring the network's functionality and validating transactions.
- Project Governance: The ownership of more tokens grants users greater influence in decision-making for project management.
Consistently ranking within the top 10 cryptocurrencies based on market capitalization, ADA reflects its widespread recognition, popularity, and sustained investor interest.
Notably, ADA stands out for its distinctive feature – it cannot be mined and is solely available for purchase. However, this characteristic offers advantages, as it eliminates the need for expensive computing power and excessive energy consumption. Instead, owning a specific quantity of tokens suffices.
In terms of cost, ADA remains relatively affordable compared to other leading digital currencies. As of the current writing, one ADA token is valued at just over $0.45 and is accessible on major cryptocurrency exchanges.
The total supply of ADA is capped at 45 billion units, with circulation occurring gradually. At present, approximately 80% of all tokens are in circulation, contributing to the coin's overall market dynamics.
Staking
As previously mentioned, Cardano's native coin, the ADA cryptocurrency, distinguishes itself by the absence of a mining process, rendering traditional miners non-existent within its blockchain. Instead, the responsibility of overseeing operations and achieving consensus on the network falls upon validators, represented by nodes or pools that uphold an up-to-date copy of the registry.
Token holders actively participate in the network through a process known as staking, akin to placing bets. In this context, users have the option to delegate a portion of their holdings to these staking pools. The selection process involves choosing from existing staking pools or, for those seeking a more hands-on approach, creating their own pool. It's worth noting that the latter option entails a more labor-intensive process.

This process brings mutual benefits to both users and the blockchain itself. Token holders not only receive rewards in the form of passive income but also contribute to enhancing the platform's functionality, reinforcing security measures, and exerting influence over the network's development.
It is crucial to grasp that the coins engaged in staking are exclusively reserved for this purpose and cannot be utilized for trading or transfers during a predetermined lock-up period, ranging from several hours to several days. Notably, the duration of the lock-up period directly correlates with the potential reward – a longer commitment resulting in a higher yield.
Participation in staking is accessible through Daedalus or Yoroi wallets. Users can easily engage by selecting a staking pool within the wallet application and transferring the desired number of tokens, granting the pool the authority to manage them on their behalf.
Choosing the right staking pool for optimal profit requires careful consideration of performance indicators such as rank, blocks produced, margin, and other relevant metrics. While the potential profitability can reach up to 36%, the average annual return typically falls within the range of 3% to 6%.
ADA vs. Ethereum
The blockchain landscape witnesses the constant emergence of new networks, raising the question of their ability to compete with established platforms. In this context, Cardano and its native token, the ADA cryptocurrency, have garnered attention as a potential "Ethereum killer." Let's delve into this comparison to discern the reality.
Cardano frequently finds itself in the shadow of Ethereum, and the connection between the two extends beyond casual observation. Charles Hoskinson, a key figure in the development of Ethereum, also played a pivotal role in Cardano's creation. To unravel the nuances of these networks, it's essential to examine their similarities and distinctions.
Both Cardano and Ethereum are distinct entities, not mere replicas or forks of existing blockchains. Originating from the ground up, each possesses its unique characteristics. Ethereum, credited with introducing smart contracts, revolutionized the blockchain space. In contrast, Cardano stands out as a pioneer in the third-generation blockchain realm, incorporating novel technologies aimed at enhancing transaction scalability and speed.
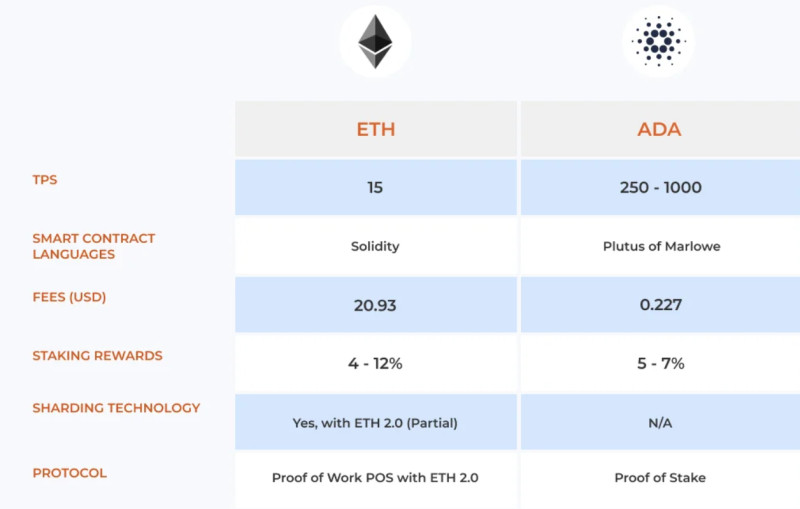
These networks employ distinct consensus algorithms: Ethereum utilizes the PoW algorithm, while Cardano adopts a PoS variant. Consequently, their throughput varies significantly; Ethereum processes around 15 operations per second, whereas Cardano boasts a potential throughput of up to 1000 transactions per second.
The divergence in consensus mechanisms manifests in how these networks handle the addition of new nodes. Ethereum experiences a slowdown as new nodes join, given that each transaction undergoes verification by all nodes. Conversely, Cardano accelerates with the incorporation of new nodes, effectively addressing the scalability challenge.
Beyond transaction speed discrepancies, the networks differ in transaction fees. Although fees are contingent on network congestion, general averages offer insights: Cardano typically maintains a fee of approximately $0.20, while Ethereum's fees can surge to $20 or more, underscoring the substantial divergence in cost between the two platforms.
Advantages and drawbacks
As observed, the Cardano blockchain stands out in comparison to first and second-generation networks, possessing distinctive strengths and weaknesses. A comprehensive analysis of these aspects follows:
Advantages:
1. Robust Team and Scientific Foundation
The project benefits from a team of accomplished scientists, leveraging their research-driven developments. Additionally, one of the founders has prior success in creating the Ethereum blockchain.
2. Scalability without Limits
Cardano's innovative approach enables the simultaneous verification of multiple transactions, offering unlimited scalability. As user numbers increase, the network efficiently handles a growing volume of transactions.
3. Environmentally Friendly Design
Employing a specialized consensus mechanism, Cardano minimizes energy consumption, distinguishing itself as an environmentally sustainable blockchain.
4. High Transaction Speeds
Cardano currently supports 1000 transactions per second, with the potential for further increases as additional validators and nodes are integrated.
5. Cost-Effective Transactions
Transaction fees on Cardano are notably lower compared to popular blockchains like Bitcoin or Ethereum, contributing to a more cost-effective user experience.
6. Two-Tier Structure
The network features a two-level structure, with one tier designated for payments and cryptocurrency exchange, while the other facilitates the development of applications and smart contracts.
Challenges and Disadvantages:
1. Ongoing Development:
Cardano is still in development, not having completed all intended stages. The realization of its goals remains uncertain, pending further progress.
2. Limited Exchange and Wallet Support:
The network's native token faces limited support on exchanges and wallets, leading users to encounter difficulties with the platform's wallet.
3. Marketing Weakness:
Despite its strong scientific foundation, Cardano has experienced challenges due to its comparatively weaker focus on marketing. The landscape often favors projects with robust promotional strategies, impacting Cardano's visibility in the market.
In summary, while Cardano demonstrates considerable strengths, the ongoing developmental phase, limited token support, and marketing strategies pose challenges that warrant careful consideration.
Development prospects
The Cardano platform and its utility token ADA has every chance for further successful development. This becomes possible thanks to a strong development team and unique technologies that were used in the implementation of this project.
The Cardano blockchain utilizes a specialized consensus algorithm, offering near-limitless scalability. With an increasing user base, transaction speed on the network accelerates significantly.
Moreover, developers prioritize cross-platform collaboration with other blockchains, integrating additional networks like sidechains to alleviate the main network's workload.
Cardano's emphasis on adhering to the legal requirements of the countries where its currency is used positions it to swiftly attain the status of a recognized legal tender. Consequently, the currency has the potential to evolve into a global social and financial system, empowering individuals across diverse regions to implement projects in agriculture, trade, education, and beyond.
This project's commitment to real-world applications seeks to enhance the lives of ordinary people, particularly those in developing countries, impacting vital areas such as insurance, deposits, loans, and more.
Furthermore, the project demonstrates strong social and environmental initiatives, making it attractive to investors. In 2021, the company allocated $6 million to sponsor African startups in the blockchain sector. Additionally, the company actively contributes to forest restoration, with 1 million trees planted in 2022.
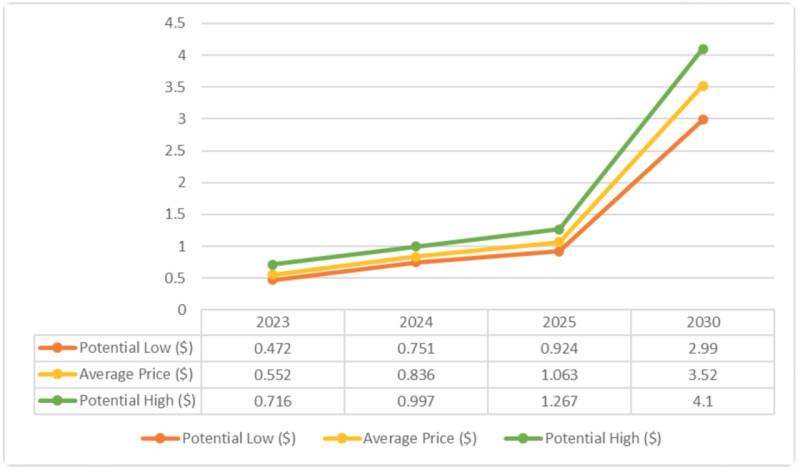
While some experts anticipate a potential 10,000% increase in the value of the ADA cryptocurrency, it's crucial to acknowledge the inherent volatility of digital currencies, susceptible to various influencing factors that may impact these predictions.
Conclusion
This article delves into the distinctive characteristics and attributes of the Cardano blockchain network and its native token, the ADA cryptocurrency. The project is rapidly evolving, captivating investors with its commitment to leveraging digital technologies for addressing tangible issues.
An instrumental figure in the development of this platform is Charles Hoskinson, who played a pivotal role in shaping Ethereum, the second-generation network. However, Cardano is hailed as more progressive, positioning itself as a third-generation blockchain.
A cadre of accomplished scientists contributed to crafting this platform, drawing upon research from leading global universities. Consequently, the technology is underpinned by robust mathematical calculations.
The platform boasts extensive scaling capabilities, facilitated by its unique consensus algorithm, Ouroboros. Validators, comprising ADA token holders and members of the Cardano community, authenticate transactions and synchronize the ledger.
As the number of validators in the blockchain grows, throughput increases, leading to faster transaction processing and reduced fees. All transaction fees are settled in Cardano utility tokens.
Furthermore, ADA ownership endows users with the opportunity to participate in company governance through voting and proposing ideas for the platform's ongoing development. Notably, ADA cryptocurrency operates without a mining process, contributing to reduced electricity consumption and associated costs.









 Back to articles
Back to articles















