
The FTT cryptocurrency is the native token of the now-bankrupt FTX international exchange, which quickly gained popularity among crypto enthusiasts.
In early December 2020, the token was priced at just $4, while 12 months later, it started trading at $45.
During the same period, FTX's market capitalization jumped from $400 million to more than $6 billion. By early 2022, it was already valued at $32 billion.
However, in November 2022, the mega-popular crypto platform FTX unexpectedly collapsed as it faced a massive liquidity crisis. As a result, its CEO and founder, Sam Bankman-Fried, hastily resigned on November 11.
In this article, we will examine the exchange's history, its token, discuss the reasons behind its rapid growth, and of course, explore the causes of the company's collapse, what eventually became of it, and what are the prospects for FTT.
FTX Exchange History

FTX is a centralized cryptocurrency exchange that, as of 2021, boasted over 1 million registered clients worldwide and had a daily trading volume of about $1 billion.
The exchange was launched in 2019 by Sam Bankman-Fried and Gary Wang.
Sam Bankman-Fried was born in 1992 in Stanford, California. In 2014, he graduated from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology with a bachelor’s degree in physics.
Then Bankman-Fried worked as a trader at Jane Street Capital in New York, where he dealt with cryptocurrency ETFs, futures, and stocks of various companies. At that time, he developed an automated system for over-the-counter trading.
In 2017, Bankman-Fried left Jane Street Capital and, together with his programmer friend Gary Wang, founded investment company Alameda Research. Initially, the FTX exchange was a service within this company. Officially, the platform entered the crypto market in 2018 but began operations only in May 2019.
The service, legally owned by FTX Trading LTD, was incorporated in Antigua and Barbuda. Bankman-Fried appointed himself as the CEO of Alameda Research, with Gary Wang as the CTO. Before creating FTX, Wang had worked at major IT companies like Facebook and Google.
The main idea behind FTX was to simplify cryptocurrency trading as much as possible. The exchange found a buyer if a client wanted to sell something and a seller if a user wanted to make a purchase.
Like all similar platforms, it profited from each user's trading transaction, offering loans (leverage) to clients willing to make substantial bets, but with increased commission fees for the risk.
The FTT cryptocurrency, created as the exchange's native token, offered numerous bonuses to its holders.
Initially, FTX launched cryptocurrency futures trading, allowing traders to speculate on the price changes of digital assets such as Bitcoin. In its first year, the platform's turnover reached $3 billion.
In July 2020, the exchange raised a colossal $8 million in a Series A funding round.
Among the investors were Paradigm, Canada's largest manufacturer of Hi-Fi and Hi-End acoustic systems, American venture fund Ribbit Capital, US hedge fund Third Point, as well as Lightspeed Venture Partners, Coinbase Ventures, Softbank, Sino Global Capital, Multicoin Capital, and others.
In September 2020, Bankman-Fried introduced spot pair cryptocurrency trading on the platform, turning it into a full-fledged crypto exchange.
By that time, the company's market capitalization reached $1.2 billion, and the monthly trading volume increased to $7 billion.
In July 2021, Sam Bankman-Fried managed to raise $900 million in a Series B funding round. This time, investors included Japanese holding company SoftBank, American venture fund Sequoia Capital, and Temasek, the largest investment company in Asia.
By then, the exchange had entered the top 5 global cryptocurrency platforms, with its market value jumping to $18 billion.
In October 2021, the head of FTX offered users to trade tokenized shares of major technology companies such as Tesla, Apple, and Facebook, attracting even more traders. By January 2022, FTX had grown to be the world's second-largest cryptocurrency exchange by trading volume, second only to Binance.
In February 2022, the company managed to raise an additional $400 million in a Series C funding round. As a result, its market value reached a mammoth $32 billion.
Key Features of FTX Platform

Before delving into the reasons for FTX's collapse, let's discuss its features.
Firstly, futures contracts were a notable feature. FTX offered futures contracts on over 80 cryptocurrencies, a figure unmatched by any other cryptocurrency platform by the end of 2021.
Secondly, the platform offered perpetual futures, allowing clients to invest in futures without an expiration date.
Thirdly, FTX offered options trading. Clients were able to choose the option they wanted and get a trading offer within 10 seconds, which they could also choose not to accept.
Fourthly, FTX featured a prediction market, enabling users to bet on real-world events such as the outcome of the US presidential election.
FTX's popularity stemmed from its attempt to address issues prevalent on other crypto exchanges, which were largely ignored elsewhere. For example, FTX was the first exchange to offer clients a simplified and more user-friendly way to trade derivatives, a feature other platforms lacked.
Before Bankman-Fried's exchange emerged, liquidity was a significant problem for most cryptocurrency platforms, making it difficult for users to enter and exit positions at desired prices.
FTX guaranteed high liquidity levels. According to CoinMarketCap, it ranked third among exchanges in terms of liquidity, trailing only behind major competitors Binance and Coinbase.
Furthermore, Bankman-Fried’s platform reduced the likelihood of clawbacks, a situation where investors' savings were taken to cover another investor's bankruptcy. Many exchanges resorted to taking funds from their private investors because returning assets outside the system was impossible.
FTX rarely faced this issue, thanks to a complex algorithm that helped liquidate trading positions, ensuring the net asset value never fell below zero.
FTX offered two separate platforms:
- for international users
- for US residents
The latter had a limited selection of coins and features. The company even partnered with LedgerX LLC to somewhat expand offerings to United States residents.
The main interface of FTX provided clients with numerous tools for trading digital assets. Platform users were able to trade cryptocurrencies and stocks in traditional and foreign exchange markets. Shortly before its collapse, the platform launched FTX Pay, a service designed for fiat currency payments.
Registration on FTX was notably straightforward, essentially its hallmark. Users needed only to fill out a basic profile and verify their identity. After verification, they were able to deposit fiat money via ACH bank transfers or credit cards, or using a digital wallet.
FTX supported leveraged tokens, allowing users to set leverage up to 101x, meaning a 1% price change could double a trader's profit.
The platform featured over 130 cryptocurrencies, including lesser-known ones.
The previously mentioned prediction market allowed clients to speculate on real-world events, which many found appealing.
FTX offered a vast array of additional orders to protect client accounts, including limit orders for stop loss, trailing stop, and take profit.
FTX’s key advantages included:
- Unique derivative instruments, setting it apart from competitors with a wide range of financial derivatives and trading opportunities.
- A user-friendly interface, making it easy for even novice traders to navigate.
- Global reach, requiring only an internet connection and a few minutes of free time to register and trade.
However, the exchange had its drawbacks:
- Limited services, as US laws prohibited residents from trading on FTX.com. To circumvent this restriction, Bankman-Fried created FTX.us, but it lacked a wide selection of derivative instruments.
- High withdrawal fees, with withdrawals under $10,000 costing an additional $75, significantly higher than on other major crypto platforms.
- Limited asset selection, forcing clients interested in popular cryptocurrencies like Polkadot, Stellar, or Cardano to look for other platforms or choose different altcoins available on FTX.
Features of FTT cryptocurrency

The FTT cryptocurrency is one of the many innovative products offered on the FTX exchange. This asset could be traded as well as used for transactions.
FTT is often referred to as one of the ERC-20 tokens. As a reminder, ERC-20 tokens are virtual coins used not on their native blockchain but on the Ethereum network. Naturally, to store these tokens, a user must have a compatible wallet.
To maintain the value of FTT coins, the FTX exchange continuously bought back and burned its tokens. FTX allocated the following funds for purchasing coins:
- 33% from commissions fees received,
- 10% from fees collected by the exchange from its insurance fund,
- 5% from other fees.
A major advantage of FTT tokens was the discount on commissions. This meant that FTT coin holders paid a lower commission on cryptocurrency futures and could benefit from tighter spreads.
For the most active traders on the FTX platform, the percentage difference could reach an impressive 60%. Additionally, traders could use FTT as collateral.
By acquiring FTT, traders automatically received insurance protection, which shielded them from clawbacks. During market volatility, such insurance guaranteed traders a net profit, meaning they could continue trading without facing margin calls.
Moreover, this insurance was extremely beneficial for leverage trading. The FTT cryptocurrency was actively used to open leveraged positions, where profits and losses were amplified according to the chosen multiplier.
Traders could stake FTT coins, where token holders could validate transactions.
In fact, staking FTT offered numerous advantages. For instance, users received additional discounts and the chance to spin the "non-fungible swag wheel," potentially winning free NFTs.
At the peak of its popularity and unwavering trust from users and investors in the asset and the exchange itself, FTT's market capitalization was approximately $6.1 billion. Before the collapse of the FTX exchange, its native token was among the top 30 largest cryptocurrencies in the world by market capitalization. Today, of course, this is no longer the case.
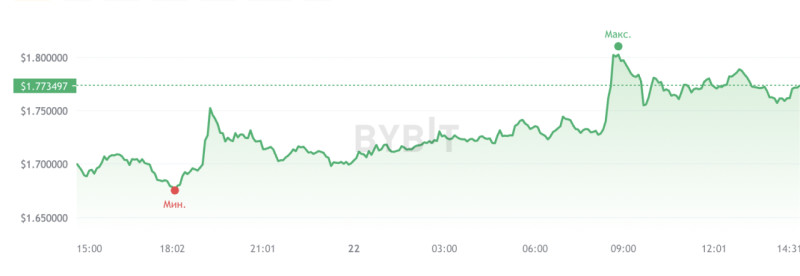
As of now, the FTT cryptocurrency is valued at $1.77 with a market capitalization of $566.65 million. At the time of preparing this material, there were 328.90 million coins in circulation.
FTX Exchange Bankruptcy
The main question in the crypto community today is why such a popular and successful cryptocurrency exchange suddenly went bankrupt.
In June 2022, Alameda Research faced media criticism, with its leaders being accused of manipulating cryptocurrency prices. From this point on, user trust in the FTX exchange was undermined, leading to a gradual withdrawal of funds.
On November 2, 2022, it was revealed that Alameda Research's balance sheet contained an illiquid FTT token worth more than $5 billion. This announcement caused panic, with users massively withdrawing their money from the platform – $6 billion was withdrawn within 72 hours.
On November 7, Binance CEO Changpeng Zhao announced his intention to acquire the FTX company. However, he abruptly changed his mind the next day, as it turned out that FTX's balance sheet had problems.
On November 11, 2022, FTX declared bankruptcy, initiating Chapter 11 bankruptcy proceedings. Sam Bankman-Fried stepped down as the head of the company, and John J. Ray took over his not-so-vacant position.

John J. Ray was a specialist in restructuring, previously handling the bankruptcy cases of US energy company Enron (bankrupted in 2001) and Canadian telecommunications equipment manufacturer Nortel Networks (dissolved in 2009).
It turned out that FTX had a colossal liquidity shortfall of $8 billion. The exchange's asset circulation scheme was dubious: digital currencies of platform users were mixed with the balance of Alameda Research and then used for issuing risky loans.
Moreover, the company's financial reporting did not reflect reality. For example, the management reported having $5.5 billion of their clients' money, but the actual amount was only $661 million.
As a result of the legal process, former CEO Sam Bankman-Fried was unanimously found guilty and is currently awaiting sentencing. The founder and former head of the FTX exchange was charged with fraud, conspiracy to commit fraud, and money laundering.
The financial losses from the collapse of the once-successful company were enormous: venture investors, including Sequoia and Softbank, suffered heavy losses, while numerous exchange clients were unable to retrieve their funds deposited on the platform. The damage to creditors was estimated at $3.1 billion.
FTX's bankruptcy led to a drop in the value of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. Witnessing an unexpected failure of the successful platform, many investors rushed to withdraw their funds from other centralized exchanges en masse. The entire crypto community feared a domino effect.
Obviously, this situation has cast significant doubt on the reliability and transparency of major centralized crypto platforms. Many experts still believe that the crypto industry must move towards decentralization. There has been a call for users to have much more control over crypto exchanges and their actual balances.
The story of the FTX exchange has become a loud and vivid example of how disregarding basic corporate governance rules and a risky business model can bring down even the most successful project in just a few months.
Why does FTT continue to gain value?

The FTX cryptocurrency exchange, which went bankrupt in 2022, continues to pay approximately $1.3 million daily in bankruptcy-related fees.
The exchange was billed at least $118.1 million for the quarter ending October 31, 2023, by numerous lawyers and various bankruptcy consultants. This means that FTX had to pay $1.3 million per day ($53,000 per hour) in bankruptcy expenses over 92 days.
Against this backdrop, the FTX exchange token has been extremely volatile. At the time of writing, it was trading at $1.77, having changed by +6.25% in the last 24 hours.
The main question is why the FTT cryptocurrency continues to gain value despite its scandalous past. After the loud bankruptcy of Bankman-Fried's company, it seemed that its native token should forever remain at the bottom. However, contrary to all these justified expectations, the FTT coin not only continued to rise but even soared in price by 300%.
The token’s uptrend was driven by comments from Securities and Exchange Commission chief Gary Gensler. He once expressed his opinion that the FTX exchange could indeed be revived, but only if the new company management operated strictly within the framework of US legislation.
On February 1, 2024, it became known that although the FTX team plans to fully settle its obligations to clients, the idea of relaunching the platform under the conditional name FTX 2.0 is not even under consideration.
Despite the cryptocurrency's scandalous reputation and the FTX platform leaving investors without money, the FTT cryptocurrency managed to recover. Although the coin currently has a relatively low market capitalization, it still has a chance to reach new highs.









 Back to articles
Back to articles















